Potato (Solanum tuberosum)
About Potato
Potatoes are underground tubers with soft flesh and endless potential. From creamy mash to crispy fries and layered gratins, they’ve earned their spot as the world’s favorite comfort carb.
They can be fluffy, waxy, or buttery — depending on type — and absorb flavor like a sponge.
The History of Potato
Potatoes were first domesticated over 7,000 years ago in the Andes Mountains, primarily in modern-day Peru and Bolivia. Spanish explorers brought them to Europe in the 1500s, where they were first met with skepticism, then rapid adoption.
They’ve since become a dietary cornerstone in every continent, deeply embedded in dishes like Irish colcannon, Indian aloo, and Peruvian papa a la huancaína.
The Science of Potato
Potatoes are high in carbohydrates, particularly starch, and provide vitamin C, potassium, and fiber (especially with skin). They contain resistant starch, which feeds gut bacteria and may help with blood sugar control.
Colored varieties offer anthocyanins, potent antioxidants.
The Geography of Potato
Today, potatoes are grown in over 100 countries — from China and India to Ukraine and the U.S. They adapt to a range of altitudes and soils, and their versatility has made them globally beloved.
In the Andes, over 4,000 traditional varieties still grow across mountain terraces.
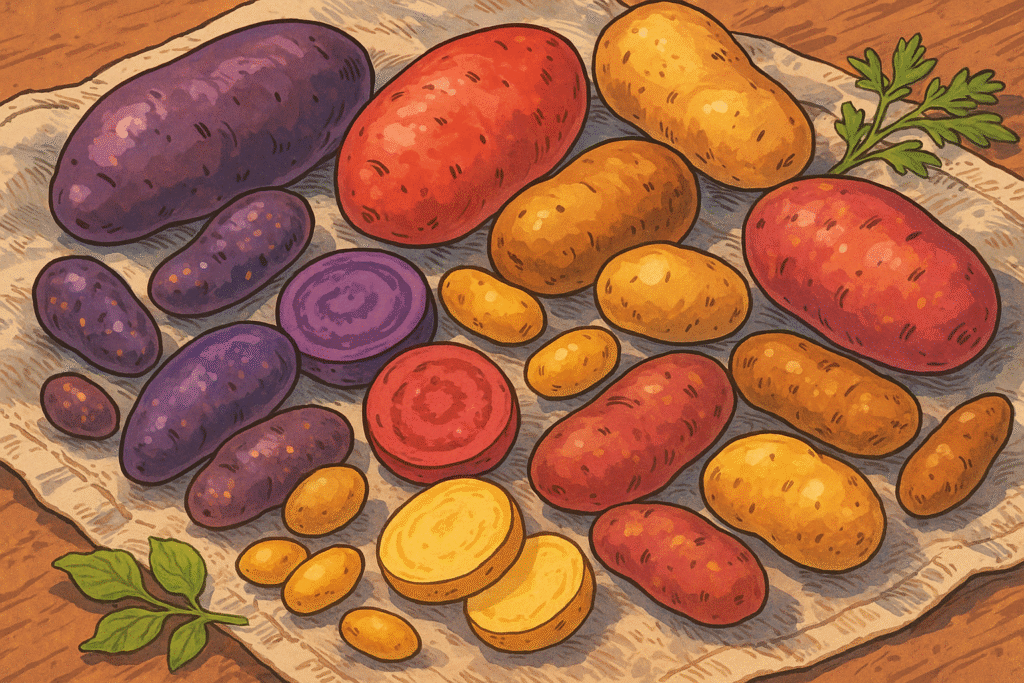
Varieties of Potato
Russet
Starchy with fluffy interior. Best for baking and fries.
Yukon Gold
All-purpose, creamy, and golden. Ideal for mashing and roasting.
Red Bliss
Waxy with thin skin. Great in salads and soups.
Purple Majesty
Deep violet inside and out. Rich in antioxidants and stunning on the plate.
Fingerling
Small, knobby, and nutty. Delicious roasted whole.
FAQs All your questions about Potato: answered
What’s the difference between waxy and starchy potatoes?
Waxy potatoes hold their shape when cooked — ideal for salads. Starchy ones break down and fluff up, perfect for mashing.
Can you eat potato skin?
Yes — it’s full of fiber and nutrients. Just scrub it well.
Are green potatoes safe to eat?
No — green skin indicates solanine, a toxic compound. Peel or discard those parts.
How should potatoes be stored?
In a cool, dark, dry place. Avoid the fridge, which can cause starch to turn to sugar.